In a very old post (Save Data To File), I wrote about writing data to and reading data from internal file storage. And that is a very very simple post about working with File Storage in Android.
In this post, I’ll show you a deeper look into the Android file storage and how to perform file-related tasks.
A - Internal Storage vs External Storage
All Android devices has 2 file storage areas:
- Internal Storage: a built-in, non-violated memory for individual app
- External Storage: a removable storage such as SD card. But nowadays, many devices divide its permanent memory into 2 part internal and external, in this case, external storage is not a "removable storage".
Comparison:
| Internal Storage | External Storage |
| Always available | Only available if the removable storage was mounted into the device |
| By default, the internal storage is only accessible by its own application | Word-readable |
| If user uninstall the application, every data in internal storage will be deleted | If user uninstall the application, all the data which was not stored in getExternalFileDir() folder will remain |
B - Work with Internal Storage
1. Write File
Firstly, you have to call Context.openFileOutput() method to open a file in internal storage and return a FileOutputStream (create new file if it doesn’t exist):
FileOutputStream fos = context.openFileOutput(fileName, Context.MODE_PRIVATE);
This method takes 2 parameters:
- name: the file's name
- mode: writing mode
- MODE_PRIVATE : file can be accessed only by the application which created it
- MODE_WORLD_READALBE : That file can be read by any application
- MODE_WORLD_WRITABLE : That file can be read and written by any application
Then, you can write the data in bytes format to created file and remember to close the stream after wrote:
public static void writeToInternalStorage(Context context, String fileName, byte[] data)
throws IOException {
FileOutputStream fos = context.openFileOutput(fileName, Context.MODE_PRIVATE);
fos.write(data);
fos.close();
}2. Read File
In order to read data from a file, you must create a FileInputStream object by calling openFileInput() method:
FileInputStream fis = context.openFileInput(fileName);
This method takes file name as the only parameter.
Then, you can read data in bytes format from the input stream and remember to close it after read:
public static byte[] readFromInternalStorage(Context context, String fileName)
throws IOException {
FileInputStream fis = context.openFileInput(fileName);
byte[] result = getBytesArrayFromInputStream(fis);
fis.close();
return result;
}
/***
* Return a bytes array from the InputStream
*/
private static byte[] getBytesArrayFromInputStream(InputStream input) throws IOException {
byte[] buffer = new byte[8192];
int bytesRead;
ByteArrayOutputStream output = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
while ((bytesRead = input.read(buffer)) != -1) {
output.write(buffer, 0, bytesRead);
}
return output.toByteArray();
}C - Work with External Storage
1. Check External Storage Availability
Because the external storage is not always available, to make sure the application works properly, we have to check if the external storage is available or not:
public static boolean isExternalStorageWritable() {
String state = Environment.getExternalStorageState();
if (Environment.MEDIA_MOUNTED.equals(state)) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
public static boolean isExternalStorageReadable() {
String state = Environment.getExternalStorageState();
if (Environment.MEDIA_MOUNTED.equals(state) ||
Environment.MEDIA_MOUNTED_READ_ONLY.equals(state)) {
return true;
}
return false;
}2. Write File
In external storage, we have 2 types of directory:
- Public: when the application was uninstalled, all the data in this directory will remain. You can refer to this directory using Environment.getExternalStoragePublicDirectory() method.
- Private: when the application was uninstalled, all the data in this directory will be deleted. You can refer to this directory using Context.getExternalFileDir() method.
You usually use public directory to store the data that can be used by other application (captured photos, downloaded files,…) and private directory for the data that is only meaningful to your app.
To write data to external storage:
- Open or create selected file
- Create Output Stream for that file
- Write data
- Close the stream after wrote
public static void writeToExternalPublicFile(String dirType, String fileName, byte[] data)
throws IOException {
File file = new File(Environment.getExternalStoragePublicDirectory(dirType), fileName);
file.createNewFile();
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file);
fos.write(data);
fos.close();
}
public static void writeToExternalPrivateFile(Context context, String dirType, String fileName, byte[] data)
throws IOException {
File file = new File(context.getExternalFilesDir(dirType), fileName);
file.createNewFile();
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file);
fos.write(data);
fos.close();
}3. Read File
To read data to external storage:
- Open the selected file
- Create Input Stream for that file
- Read data from the Input Stream
- Close the stream after read
public static byte[] readFromExternalPublicFile(String dirType, String fileName)
throws IOException {
File file = new File(Environment.getExternalStoragePublicDirectory(dirType), fileName);
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
byte[] result = getBytesArrayFromInputStream(fis);
fis.close();
return result;
}
public static byte[] readFromExternalPrivateFile(Context context, String dirType, String fileName)
throws IOException {
File file = new File(context.getExternalFilesDir(dirType), fileName);
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
byte[] result = getBytesArrayFromInputStream(fis);
fis.close();
return result;
}D - Demo Application and Source Code
To apply the above codes, we will make a small demo application to show you how to work with File Storage in Android.
The application has 4 button to invoke different functions about read and write data in internal and external storage and a text view to display result:
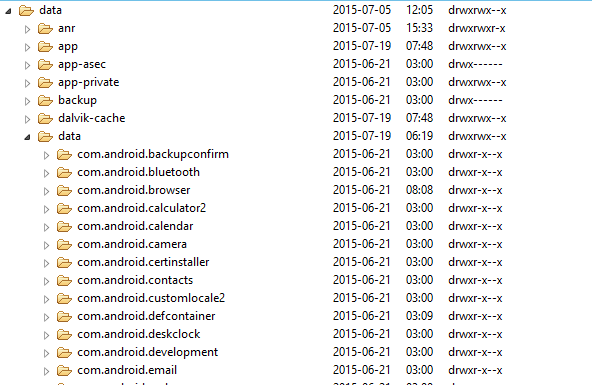
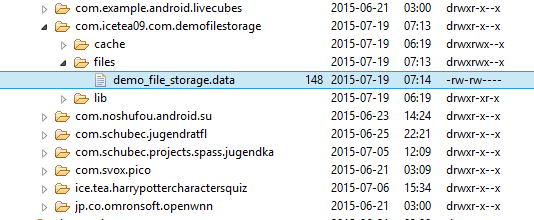
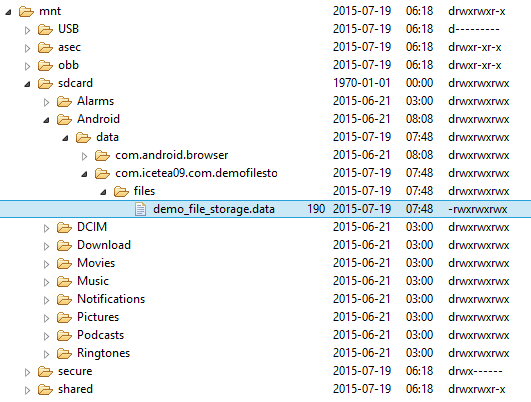
After run the application, you can look up the file in device’s storage:
Internal:
External:
The whole source code can be found at my Github: